Globe valve vs gate valve: similar functions, but cannot be used at will.
Globe valve vs gate valve are two of the most common and similar valves. Many users, especially beginners, often have a question: they both seem to be used for “opening and closing”, so can they be used interchangeably?
The answer is: although it can be temporarily replaced under some extremely loose conditions, it is absolutely not recommended to mix and match in principle. The wrong choice of valve will lead to low system efficiency, increased energy consumption, and even serious safety accidents related to globe valve and gate valve.
To understand why this is not a mix, we need to look at the core differences between them.
Understanding the differences between a globe valve and gate valve is crucial for selecting the right valve for your application.
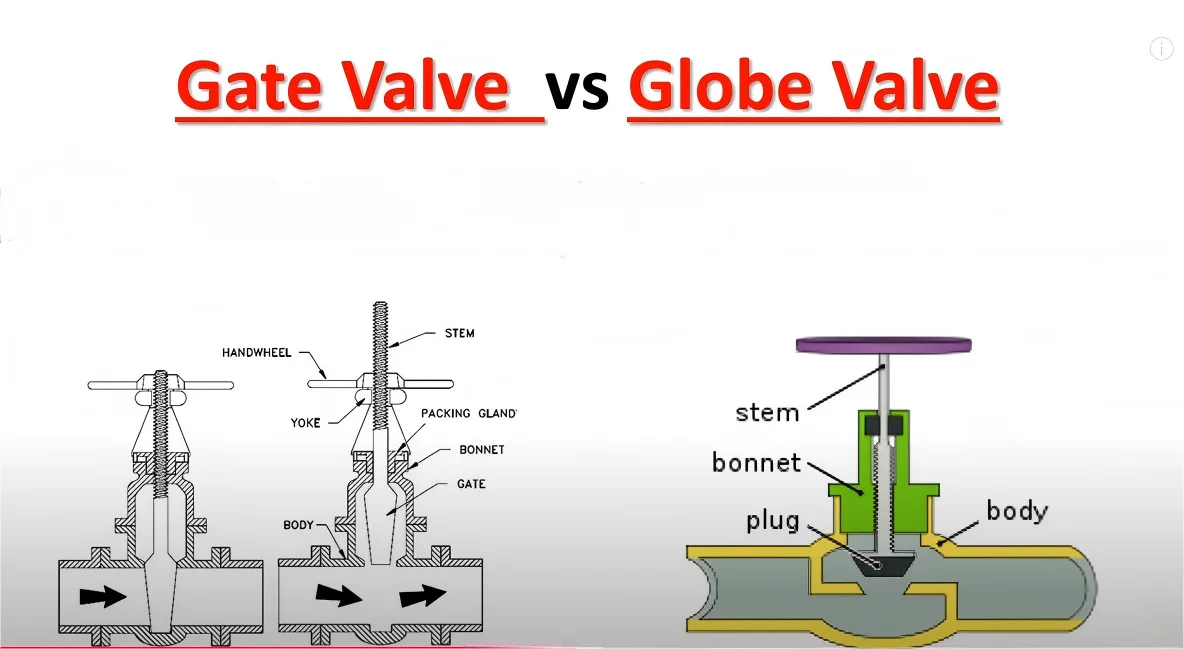
Essential differences in core structure and working principle
This is the basis for understanding that they cannot be used together.
globe valve:
Structure: There is a Z-shaped or spherical partition inside the valve body, and a disc-shaped or conical valve disc in the middle connected to the valve stem. By rotating the handwheel, the valve stem drives the valve disc to move vertically in the direction of the fluid, so as to press or leave the valve seat to realize opening and closing and adjustment.
Working mode: Adjustable and cut off. It can precisely control the opening, regulate the flow like a faucet, and provide a tight shut-off.
gate valve:
Structure: There is a wedge or parallel gate in the valve body. By turning the handwheel, the valve stem drives the gate to move vertically up and down in the direction of the fluid, like a gate rising or falling.
Operation mode: full on or full off. It is designed to allow the fluid to be completely open or completely closed, and its structure is not suitable for flow regulation.
Comparison of key performance: Why can not be mixed?
| characteristic | globe valve | gate valve | Consequence analysis of mixing |
| flow control | Excellent. The distance between the valve disc and the valve seat can be precisely controlled to control the flow. | The difference is extreme. When partially opened, the gate will produce violent erosion and vibration to the fluid, which is easy to damage the sealing surface, resulting in valve failure and internal leakage. | Do not use gate valves for adjustment. This is the most common mistake and can quickly destroy the valve. |
| Size of flow resistance | High. Due to the S-shaped flow channel, the fluid direction changes many times, and the pressure loss (pressure drop) is large. | Very low. When fully open, the flow channel is straight through and the gate is fully raised, and the resistance is close to that of the pipe itself. | The wrong use of stop valve on the main pipeline which needs low flow resistance and energy saving will lead to unnecessary increase of pump energy consumption. |
| Opening speed | Shorter (shorter trip). | Long (long journey). | Gate valves are not advantageous in situations where rapid switching is required. |
| tightness | Generally good, the valve disc and valve seat sealing surface is not easy to be washed by the flowing medium. | It works well when fully open and closed, but the sealing surface is easy to damage during adjustment and use, resulting in internal leakage. | Misuse can lead to ineffective sealing of both. |
| Installation direction | There is a direction! The valve body usually has an arrow indicating the direction of the medium flow, must be installed in the direction (usually low in high out). | No directionality. The medium can flow in from either side. | If the shut-off valve is installed in reverse, it will be extremely difficult to open, or even unable to open, and seriously damage the valve. |
| main application | Adjustment, throttling, frequent operation occasions. Such as: flow adjustment, pressure, sampling port, instrument valve, etc. | Full open or full close, infrequent operation occasions. For example: main pipeline isolation, equipment isolation, long-term maintenance of full open state. | Functional mismatch. Let those who are suitable for adjustment do the work of isolation (they can do it but cost energy), and let those who are suitable for isolation do the work of adjustment (they will soon be scrapped). |
When can “temporary substitution” be made?
Temporary replacement can be considered only in one very special and helpless situation: a gate valve in the system is completely damaged, and a globe valve of the same pressure class and diameter is needed to temporarily achieve the function of “full open” or “full close” to maintain the short-term operation of the system, and the correct valve is planned to be replaced as soon as possible.
Please note that even temporary substitution requires ensuring that:
The globe valve must be installed correctly (note the flow direction).
It is only used to “on” or “off” and must not be used for adjustment.
Accept the fact that there is a large pressure drop at the point of the system.
How to choose the right model? Summary and guide
The selection of valves is not based on convenience, but on functional requirements.
Please select the globe valve when you need:
Adjust the flow or pressure.
Need to be turned on and off frequently.
The valve is allowed to have a large pressure loss.
Applications where leakage from the valve stem stuffing box is less likely (the pressure of the globe valve can be discharged upward).
Please choose the gate valve when you need:
Complete cut off or connection of fluid, and no adjustment is required.
Low flow resistance and pressure drop requirements (e.g., pump outlet, main pipe).
The valve is open or closed for a long time and the operation is not frequent.
conclusion:
The globe valve and gate valve are fundamentally different in their structure and working principle, resulting in completely different performance and use. It is a technical error to mix them or replace them incorrectly, which will reduce system efficiency, increase operating costs, significantly shorten valve life and create safety risks.
Remember a simple principle: to adjust, use globe valve; to isolate, use gate valve. In the design and maintenance of pipeline system, strict compliance with this principle is the key to ensure the safety, efficiency, long-term stable operation of the system.
